Discretize by Binning
This transform converts a continuous variable into a categorical variable by dividing the column values into several intervals or bins, where each bin is a tuple that specifies the range of values that should be in that bin.
tags: [“Data Preparation”]
Parameters
The table gives a brief description about each parameter in Discretize by Binning transform.
- Name:
By default, the transform name is populated. You can also add a custom name for the transform.
- Input Dataset:
The file name of the input dataset. You can select the dataset that was uploaded from the drop-down list. (Required: True, Multiple: False)
- Output Dataset:
The file name with which the output dataset is created with group values based on the specified bins. (Required: True, Multiple: False)
- Column Name:
The column to discretize. (Required: True, Multiple: False, Datatypes: [“STRING”], Options: [‘FIELDS’], Datasets: [‘df’])
- Number of bins:
The number of bins that contains the group values. (Required: True, Multiple: False, Datatypes: [‘LONG’], Options: [‘CONSTANT’])
The sample input for this transform looks as below:
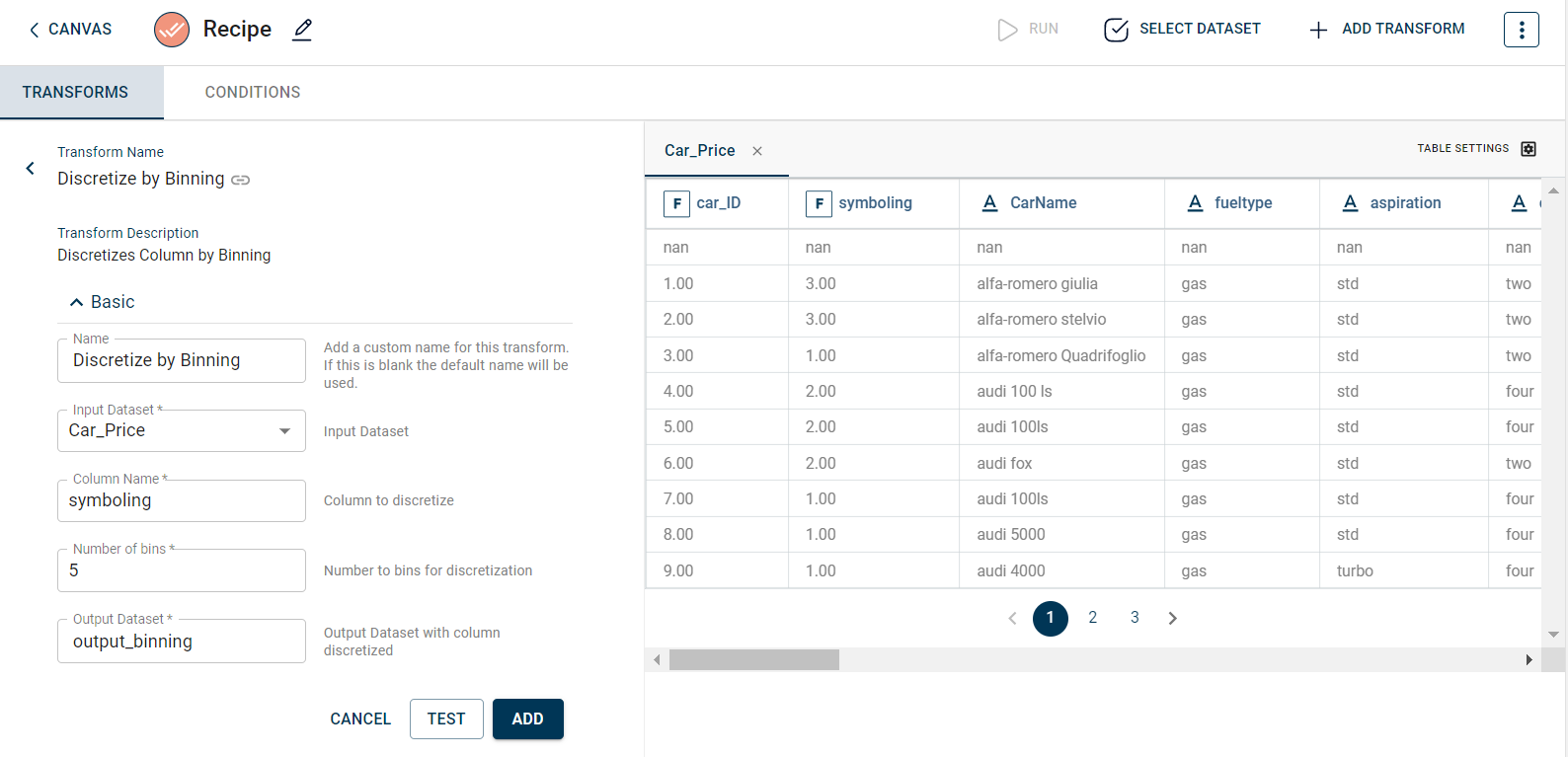
The output after running the Discretize by Binning transform on the dataset appears as below:
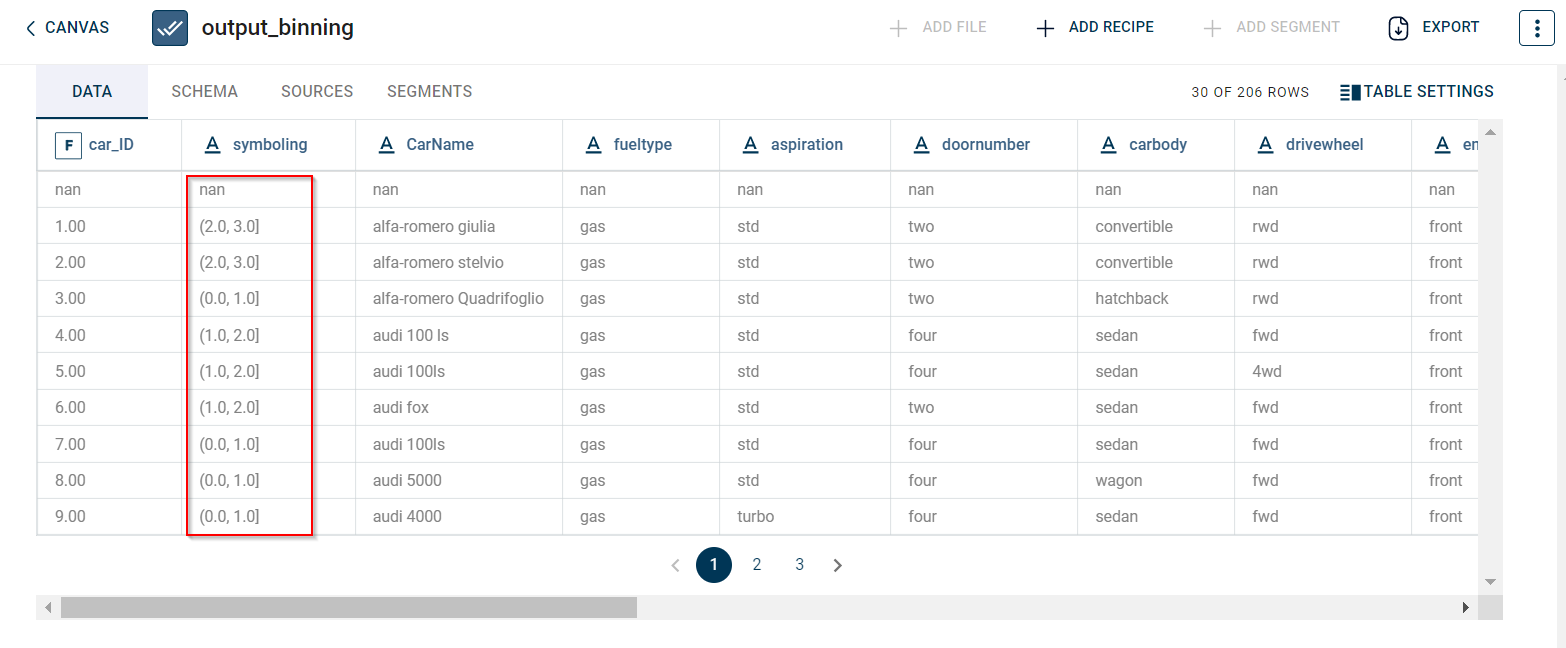
How to use it in Notebook
The following is the code snippet you must use in the Jupyter Notebook editor to run the Discretize by Binning transform:
template=TemplateV2.get_template_by('Discretize by Binning')
recipe_Discretize_by_Binning= project.addRecipe([car_data, employee_data, temperature_data, only_numeric], name='Discretize by Binning')
transform=Transform()
transform.templateId = template.id
transform.name='Discretize by Binning'
transform.variables = {
'input_dataset':'car',
'output_dataset':'car_binning',
'col':"enginesize",
'n':3}
recipe_Discretize_by_Binning.add_transform(transform)
recipe_Discretize_by_Binning.run()
Requirements
pandas